You can learn about what mathematical ideas your child is working on by exploring the resources found in each of the nine weeks below. You will find video clips, examples of student work, and games/activities to try at home!
Third Grade Unpacking Document
Major Work Standards
Third Grade Student Discussion Videos
Third Grade Parent Information from NCDPI
Third Grade Unpacking Document
Major Work Standards
Third Grade Student Discussion Videos
Third Grade Parent Information from NCDPI

First Quarter
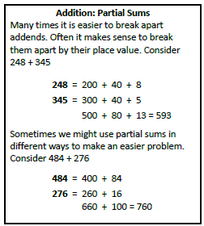
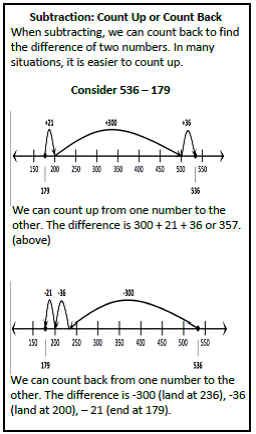
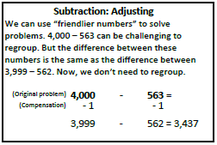
During the first nine weeks, your third graders will be extending ideas about the structure of the place value system, adding and subtracting using strategies based on place value. They will build an understanding of the relationship between addition and subtraction as they build computational fluency. They will develop mental math strategies with an emphasis on making reasonable estimates. The use of accessible algorithms that highlight place value and algebraic ideas is the focus of this work. Students will study the traditional US algorithms in fourth grade after they have developed a solid understanding of the ideas behind the short cuts. Videos Books to Read Games Capture 5 Capture on the 300 Chart Close to 100 Online Games Student Work Samples |

Second Quarter
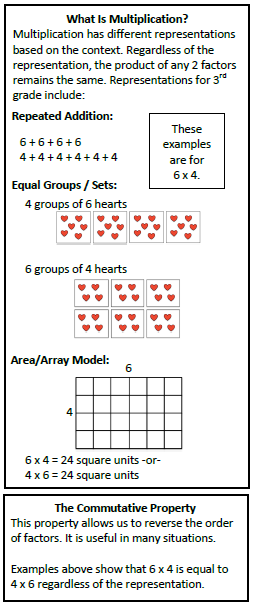
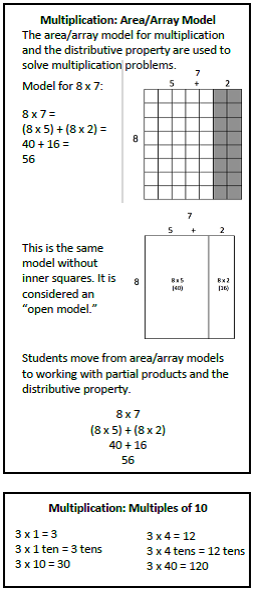
During the second nine weeks, your third graders will be exploring the properties of polygons, especially quadrilaterals. Students will build an understanding of the measurement concepts of perimeter and area, and be able to distinguish between area and the linear measurement of perimeter. They will have multiple opportunities to measure the area of a shape by finding the total number of same size units. During this quarter, students will also develop an understanding of the meanings of multiplication and division of whole numbers through activities and problems involving equal-sized groups, arrays, and area models. Students investigate the properties of multiplication and division, examine the relationship between these two operations, and develop strategies for solving multiplication and division problems. (See Multiplication and Division charts below for examples of models and strategies.) After building the foundation for what it means to multiply and divide, your third graders will work on fluency with multiplication and division within 100. (See information below from the NC Standards Unpacking document. Also see "Fluency" Section on the K-5 Mathematics Home Page.) |
Solution Strategies
Addition and Subtraction
Multiplication and Division